Expertise
Pacemakers
At ARAVIND HEART CARE, we offer Pacemaker Implantation as a safe and effective solution for patients suffering from arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), particularly bradycardia (slow heart rate) or heart block.
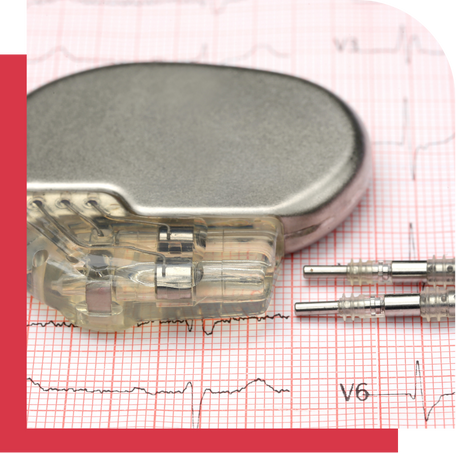
A pacemaker is a small, battery-powered device that helps regulate your heartbeat, ensuring it beats at a normal rate and rhythm. With Dr. C.S. Aravind’s expertise in pacemaker procedures, we provide comprehensive care, from diagnosis to implantation and long-term monitoring.
What Is a Pacemaker?
A pacemaker is a small device implanted under the skin, typically near the chest, to regulate abnormal heart rhythms. The pacemaker sends electrical impulses to the heart to ensure it beats at a normal pace. It is used for patients whose heartbeats are too slow (bradycardia) or whose hearts pause unexpectedly due to heart block or other conduction disorders. Pacemakers can be temporary or permanent, depending on the patient’s condition.
When Is a Pacemaker Needed?
A pacemaker may be recommended if you experience:
- Bradycardia: A slow heart rate, often causing symptoms like dizziness, fatigue, or fainting.
- Heart Block: A condition where the electrical signals between the heart's chambers are delayed or blocked, leading to irregular rhythms.
- Atrial Fibrillation: An irregular and often fast heartbeat that can lead to blood clots, stroke, or heart failure.
- Heart failure: In certain cases, pacemakers are used to improve the coordination of heart muscle contractions.
If you experience symptoms like fainting, extreme fatigue, or shortness of breath, a pacemaker might be necessary to regulate your heart’s function
How Does Pacemaker Implantation Work?
The pacemaker implantation procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia with sedation. A small incision is made below the collarbone, and the leads are inserted through a vein and attached to the heart. The pacemaker device is then placed under the skin, and the leads are connected to it. Once in place, the pacemaker monitors the heart’s rhythm and delivers electrical impulses when needed to maintain a steady heartbeat.
Types of Pacemakers
- Single-chamber Pacemaker: Sends electrical signals to one chamber of the heart, typically the right ventricle.
- Dual-chamber Pacemaker: Sends electrical signals to both the right atrium and the right ventricle, coordinating the timing between the two chambers.
- Biventricular Pacemaker: Also known as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), this pacemaker sends signals to both ventricles, often used in heart failure patients to improve heart function.
Benefits of Pacemaker Implantation
- Regulates Heart Rhythm: Ensures the heart beats at a normal rate, preventing symptoms like fainting and fatigue.
- Improves Quality of Life: Reduces symptoms of heart rhythm disorders, allowing you to engage in daily activities without fear of complications.
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure is quick, with most patients returning home the same day or the day after surgery.
- Long-lasting: Modern pacemakers are designed to last for several years and can be adjusted or replaced as needed.
Post-Procedure Care
After pacemaker implantation, you will be monitored for a short time to ensure the device is functioning properly. Most patients can return to normal activities within a few days, although you may need to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for a few weeks. Regular follow-up appointments will be scheduled to check the pacemaker and ensure it’s working as intended.
FAQs
Most pacemakers last between 5 to 15 years, depending on the type of device and your heart’s needs. Regular check-ups will ensure the pacemaker is functioning properly and can be replaced when necessary.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia with sedation, so you shouldn’t feel pain during the implantation. You may experience mild discomfort or soreness at the incision site after the procedure, but this usually subsides within a few days.
Yes, after a short recovery period, most patients can return to their normal activities, including light exercise. However, you should avoid heavy lifting and contact sports that could damage the pacemaker. Your doctor will provide specific guidelines based on your condition.
Most patients do not feel the pacemaker delivering electrical impulses. In rare cases, you might feel a slight flutter when the pacemaker corrects your heart rhythm, but this is typically not uncomfortable.
Most household electronics, including microwaves, cell phones, and computers, are safe to use with a pacemaker. However, you should avoid close contact with strong magnetic fields, such as MRI machines, unless your pacemaker is specifically designed to be MRI-compatible.
Most patients can return to work within a week, depending on the nature of their job. Jobs that involve heavy lifting or physical labor may require a longer recovery period. Your doctor will advise you on when it’s safe to resume your normal activities.
Yes, regular follow-up appointments are essential to ensure the pacemaker is functioning properly. These check-ups typically occur every 6 to 12 months.
Yes, you can travel with a pacemaker. You should inform airport security about your pacemaker, as it may trigger metal detectors. Carrying a pacemaker ID card is also recommended.
Pacemaker implantation is generally safe, but like any medical procedure, it carries some risks, including infection, bleeding, or device malfunction. Dr. C.S. Aravind and the team at ARAVIND HEART CARE take every precaution to minimize these risks.