Expertise
Angioplasty
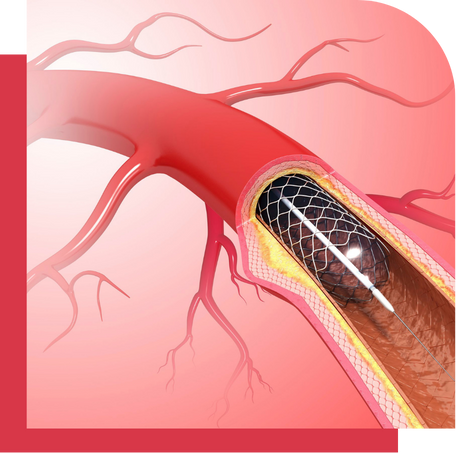
Angioplasty is a life-saving treatment for patients with coronary artery disease (CAD), which can lead to heart attacks if left untreated. Dr. C.S. Aravind, an expert in interventional cardiology, performs angioplasty with precision, offering patients a quick recovery and improved heart function.
What Is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a procedure used to treat narrowed or blocked coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. During the procedure, a small balloon is inflated inside the artery to widen it, allowing blood to flow more freely. In many cases, a stent (a small metal mesh tube) is placed in the artery to keep it open permanently.
Angioplasty is an effective treatment for patients with chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or those who are at risk of heart attacks due to blocked arteries.
How Does Angioplasty Work?
Types of Stents
- Bare-metal stents (BMS): A simple metal stent used to keep the artery open.
- Drug-eluting stents (DES): A stent coated with medication that slowly releases into the artery to reduce the risk of re-narrowing (restenosis).
Dr. C.S. Aravind will recommend the most appropriate type of stent based on your condition.
Benefits of Angioplasty
- Minimally Invasive: Unlike open-heart surgery, angioplasty is performed using small incisions, resulting in less pain and quicker recovery.
- Restores Blood Flow: Improves oxygen supply to the heart, reducing symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath.
- Prevents Heart Attacks: In emergency cases, angioplasty can quickly restore blood flow during a heart attack, reducing damage to the heart muscle.
- Short Recovery Time: Most patients are discharged within 24 hours and can return to normal activities within a week.
Recovery After Angioplasty
- Avoiding strenuous activities for a few days.
- Taking prescribed medications, including blood thinners, to prevent blood clots.
- Regular follow-up appointments to monitor heart health and ensure the stent is working properly.
- Aldosterone antagonists: To help the body eliminate excess fluid.
Lifestyle Changes After Angioplasty
- Heart-healthy diet: Reduce salt, fat, and cholesterol intake to prevent plaque buildup.
- Regular exercise: Engage in moderate physical activity to strengthen the heart.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking is crucial to improving overall heart health.
- Medication adherence: Take prescribed medications to control blood pressure, cholesterol, and prevent blood clots.